Key Takeaways
- Societies are coming together to support sustainability, applying political pressure to achieve an enormous economic shift towards net zero.
- However, the rate of change is accelerating on multiple fronts, and has the potential to create unprecedented instability.
- The minerals needed to scale greener technologies are concentrated in a small number of nations, where industrialization is driving water scarcity.
- Along with trade conflicts, new forms of warfare and terrorism – both physical and cyber – will arise, in part related to climate change.
Accelerated change, increased instability
The pace of transformation, climate change and decreasing trust in traditional institutions has the potential to create global instability and conflict. Alongside increased cyberterrorism, new forms of conflict will arise, related to the race for critical commodities to fuel energy transition, agricultural nationalism and climate change targets.
Basic systems like democracy and capitalism are also set to undergo dramatic change. However, while extremist views persist, the vast majority of the world’s population straddles the middle ground. And at a time when the power of the individual has never been greater, people have often shown a capacity to rally behind issues that benefit society at large.
“In many cases, we believe the roots of the rising conflicts stem from collective challenges for the human race, and we see a strong potential for collaboration to solve those problems.”
Robert Kwan
Energy Infrastructure Analyst, RBC Capital Markets
Net zero and climate change
Energy transition is firmly underway – a monumental economic shift with far-reaching consequences. For automakers, electrification is now the consensus view, but the scale of investment required will have large geopolitical ramifications.
Part of the problem lies with critical components, particularly the rare minerals and metals required not only for batteries, but also for many other cleaner, greener technologies, that are concentrated in a small number of nations, often with profound governance and security problems.
Sustainable solutions, security challenges
Securing supply chains of sustainable minerals will be critical to ensure innovation in key enterprises. Renewable natural gas, waste fuel, hydrogen and many more innovations will drive energy transition, as companies seek to reduce waste and carbon emissions. Packaging, recycling, shipping and logistics will seek to get to net zero and capital markets will expand green financing solutions.
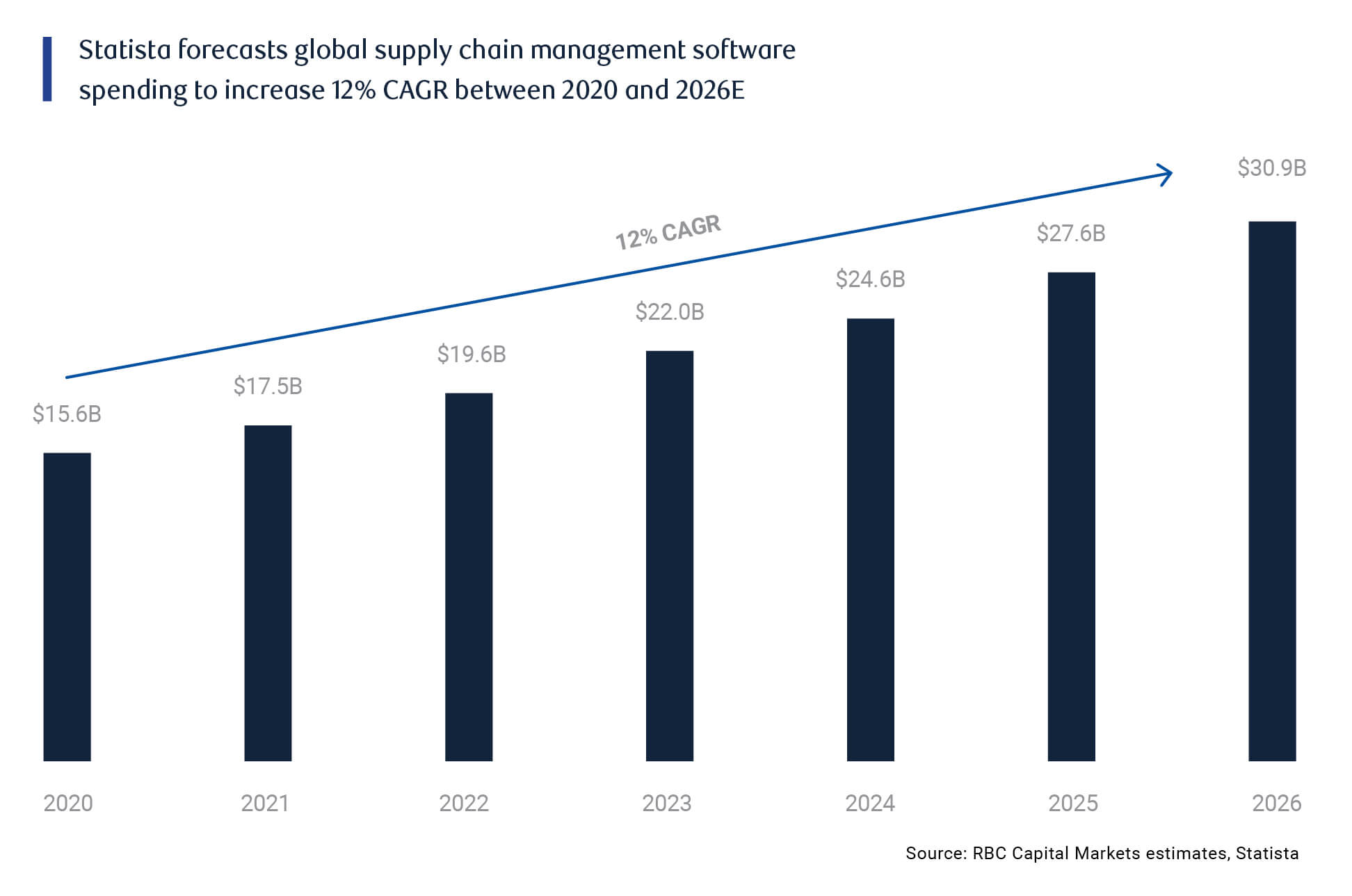
Throughout it all, security in every sense will increase in importance. Secured supply chains of critical minerals, cybersecurity in the enterprise, the security of intellectual property to ensure leadership in key areas of innovation, such as biotechnology.
“Apparel rental and resale is gaining in importance as consumers look for greater circularity in fashion, while technologies such as blockchain and NFTs can allow for the sharing of provenance details.”
Piral Dadhania
Luxury Goods Analyst, RBC Capital Markets